Weekly Digest: Python 2, Functools, data tools, and ETag headers
2to3 and six libraries
The 2to3 library is designed to help transform python 2 code into python 3 compatible code. The six library lets you import functions that work in both python 2 and 3, and it handles the compatibility between both.
Steps for working through python 2/3 conflicts
- find each conflict in a repository using 2to3
- if py3 replacement works in py2, overwrite the code to py3 version
- Else, overwrite to the
sixversion which is compatible in both py2 and py3 - transition to py3 for your project
- overwrite the
sixverions you added in step 3 to py3 versions
Example of a 2to3 fixer you can run to transition python 2 assert statements to their equivatent in python 3: https://docs.python.org/3/library/2to3.html#2to3fixer-asserts
functools.partial
functools.partial() allows you take a multiparam function and prefill some params, effectively creating another function with fewer params. So let’s say you have a function f1(x,y,z) by doing f2 = functools.partial(f1, 1, 2) you are creating a function for which f1(1,2,3) and f2(3) are equivalent.
In [1]: import functools
In [2]: def f1(x, y, z):
...: print(x, y, z)
...:
In [3]: f2 = functools.partial(f1, 1, 2)
In [4]: f1(1, 2, 3)
1 2 3
In [6]: f2(3)
1 2 3
static methods
- do not use staticmethod in a class if you can make it a module function
- do not use module function if you can just use inner body function multiple times in less lines of code https://stackoverflow.com/a/11788267
Notes on data tools
- Apache
- Hadoop = batch processing, FOSS implementation of MapReduce (Java)
- Storm = realtime stream processing (Clojure)
- Cassandra = distributed NoSQL database, wide column store (key/val + tabular)
- Kafka = realtime stream processing (Scala and Java)
- Video covering Apache Storm, and Apache Hadoop, Apache Kafka
- “Big data” 3 V’s
- Velocity (24/7 and read/write often)
- Variety (data types and structured/unstruct)
- Volume (tera-, peta-, exa-, zetta-, yotta- bytes). Grande.
- “Big data” 3 V’s
- Hadoop
- distrib. storage, processing, clusters of hardward, 1000s of machines, parallelization. HDFS (replication of blocks) and MapReduce (parallel processing - Master/Worker nodes, Jobs, Mappers, Reducers, Tasks).
- In Soviet Russia Hadoop, processes are sent to where data is stored.
- I don’t remember why I wrote this but it was funny at the time.
- fault toleranace
- Storm
- realtime (not batch)
- processes streams of data
- Storm takes care of queues! i.e. if data is piling up on one Bolt
- Java, Closure, and Python
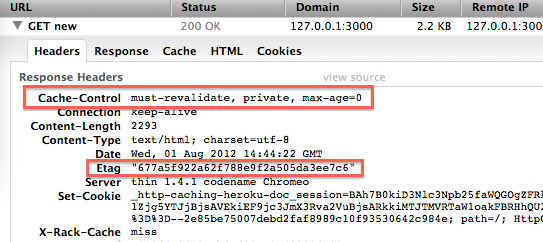
ETag headers explained with 🍔 and 🌭

- Customer orders “the special”
- Server serves 🍔 with e-tag ID 1
- Customer orders “the special” again with “if-none-match” etag 1 (I only want new special, satisfied with having 🍔)
- Server says e-tag same “304 not modified”, still 🍔
- Customer says cool I already have that NVM
- Later, customer orders “the special”
- Server says e-tag no longer 1, it’s ABC
- Server serves new “special” which is now 🌭
Problem: e-tags are generated per server (I.e. by Apache). If reverse proxy (like load balancer) get serves etag from server A, and next request matched etag against server B, “none-match” might be true. The two waiters aren’t talking to each other about the numbers they give out for the “special”, yet it might still just be a 🍔 which causes re-serve of same special. Waste of food, time, energy.
Problem: some servers will fake the “304 not modified” just so they can force the client to always send the same e-tag… Across sessions and logouts! Basically identifying the user by their cache ID. Bad. This circumvents cookies which are under users control.